The Impact of Postoperative CT Parameters on Functional Outcomes in Joint Depression-Type Calcaneal Fractures Fixed with Sinus Tarsi Locking Plate: A Retrospective Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56929/jseaortho-2025-0239Keywords:
Calcaneus fracture, Postoperative CT, Sinus tarsi locking plateAbstract
Purpose: To examine the correlation between postoperative computed tomography (CT) parameters and functional outcomes in patients treated with sinus tarsi locking plates for joint depression-type calcaneal fractures.
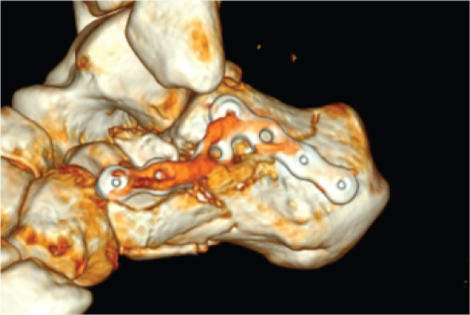
Methods: This study retrospectively analyzed patients who underwent sinus tarsi locking plate fixation for joint depression-type calcaneal fractures at a tertiary hospital between 2019 and 2021. The patients were followed up for an average of 16 months. Collected data included demographic information and postoperative CT parameters, including Böhler’s angle and posterior facet congruity. Functional outcomes were evaluated using the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM) score.
Results: Postoperative CT scans were used to evaluate the quality of fracture reduction in 55 patients with calcaneal fractures treated with sinus tarsi locking plates. The mean FAAM score was 79.4 (range: 42–100). Among the patients, 45 (82%) achieved good functional outcomes, while 10 (18%) had poor outcomes, with no significant demographic differences between groups. Anatomical, near-anatomical, and poor reduction of the posterior facet were observed in 49%, 31%, and 20% of cases, respectively. Böhler’s angle was >20º and <20º in 76% and 24% of cases, respectively. Anatomical reduction of the posterior facet showed a significant correlation (P=0.025) with favorable outcomes, whereas Böhler’s angle showed no significant association (P=0.685).
Conclusions: Sinus tarsi locking plate fixation is effective in achieving satisfactory posterior facet reduction and functional outcomes for joint depression-type calcaneal fractures. Postoperative CT scans can help predict functional recovery by evaluating posterior facet reduction. Achieving posterior facet anatomical reduction is essential for favorable functional recovery.
Metrics
References
Allegra PR, Rivera S, Desai SS, et al. Intra-articular calcaneus fractures: current concepts review. Foot Ankle Orthop 2020;5:2473011420927334. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/2473011420927334
Razik A, Harris M, Trompeter A. Calcaneal fractures: Where are we now?. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr 2018;13:1-11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-017-0297-3
de Vroome SW, van der Linden FM. Cohort study on the percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. Foot Ankle Int 2014;35:156-62. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100713509804
Schepers T. The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review. Int Orthop 2011;35:697-703. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1223-9
Busel G, Mir HR, Merimee S, et al. Quality of reduction of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures using a sinus tarsi versus extensile lateral approach. J Orthop Trauma 2021;35:285-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000001971
Li L hua, Guo Y zhi, Wang H, et al. Less wound complications of a sinus tarsi approach compared to an extended lateral approach for the treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fracture: A randomized clinical trial in 64 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e4628. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000004628
Wang Z, Wang XH, Li SL, et al. Minimally invasive (sinus tarsi) approach for calcaneal fractures. J Orthop Surg Res 2016;11:164. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-016-0497-4
Zhang G, Ding S, Ruan Z. Minimally invasive treatment of calcaneal fracture. J Int Med Res 2019;47:3946-54. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060519853402
Sato K, Yorimitsu M, Uehara T, et al. Comparison of screw versus locking plate fixation via sinus tarsi approach for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Surg 2023;29:97-102. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fas.2022.11.002
Kir MC, Ayanoglu S, Cabuk H, et al. Mini-plate fixation via sinus tarsi approach is superior to cannulated screw in intra-articular calcaneal fractures: A prospective randomized study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2018;26:2309499018792742. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/2309499018792742
de Muinck Keizer RJO, Beerekamp MSH, Ubbink DT, et al. Systematic CT evaluation of reduction and hardware positioning of surgically treated calcaneal fractures: a reliability analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2017;137:1261-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2744-5
Qiang M, Chen Y, Zhang K, et al. Measurement of three-dimensional morphological characteristics of the calcaneus using CT image post-processing. J Foot Ankle Res 2014;7:19. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-1146-7-19
Roll C, Schirmbeck J, Müller F, et al. Value of 3D reconstructions of CT scans for calcaneal fracture assessment. Foot Ankle Int 2016;37:1211-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100716660824
Sanders R, Vaupel ZM, Erdogan M, et al. Operative treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures: long-term (10-20 Years) results in 108 fractures using a prognostic CT classification. J Orthop Trauma 2014;28:551-63. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000000169
Arunakul M, Arunakul P, Suesiritumrong C, et al. Validity and reliability of Thai version of the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM) subjective form. J Med Assoc Thai 2015;98:561-7.
Carcia CR, Martin RL, Drouin JM. Validity of the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure in athletes with chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train 2008;43:179-83. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-43.2.179
Li Y, Tsang RCC, Liu D, et al. Applicability of cutoff scores of Chinese Cumberland Ankle Instability Tool and Foot and Ankle Ability Measure as inclusion criteria for study of chronic ankle instability in Chinese individuals. Phys Ther Sport 2021;48:116-20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ptsp.2020.12.021
Meng Q, Wang Q, Wu X, et al. Clinical application of the sinus tarsi approach in the treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fracture. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e0175. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000010175
Mehta CR, An VVG, Phan K, et al. Extensile lateral versus sinus tarsi approach for displaced, intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 2018;13:243. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0943-6
Eelsing R, Aronius LB, Halm JA, et al. Implant choice and outcomes of the sinus tarsi approach for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Int 2023;44:738-44 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/10711007231176276
Mulcahy DM, McCormack DM, Stephens MM. Intra-articular calcaneal fractures: effect of open reduction and internal fixation on the contact characteristics of the subtalar joint. Foot Ankle Int 1998;19:842-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/107110079801901209
Sangeorzan BJ, Ananthakrishnan D, Tencer AF. Contact characteristics of the subtalar joint after a simulated calcaneus fracture. J Orthop Trauma 1995;9:251-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00005131-199506000-00012
van Hoeve S, de Vos J, Verbruggen JPAM, et al. Gait analysis and functional outcome after calcaneal fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2015;97:1879-88. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.N.01279
Sayyed-Hosseinian SH, Shirazinia M, Arabi H, et al. Does the postoperative quality of reduction, regardless of the surgical method used in treating a calcaneal fracture, influence patients' functional outcomes?. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2023;24:562. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-023-06697-z
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The Royal College of Orthopaedic Surgeons of Thailand

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






